JDBC获取数据库连接
项目结构如下
一、获取与数据库的连接
1、通过修改配置文件,可以修改与数据库连接的信息:url,user,password
@Test
public void getConnection() throws Exception{
String driverClass = null;
String jdbcUrl = null;
String user = null;
String password = null;
//读取类路径下的jdbc.properties 文件
InputStream in = getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
driverClass = properties.getProperty("driver");
jdbcUrl = properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
user = properties.getProperty("user");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
Driver driver = (Driver) Class.forName(driverClass).newInstance();
Properties info = new Properties();
info.put("user", user);
info.put("password", password);
Connection connection = driver.connect(jdbcUrl, info);
System.out.println(connection);
}
2、通过Driver实现与数据库的连接,Driver是一个接口,可以通过重载的getConnection()方法获取数据库的连接,可以同时管理多个驱动程序,
若注册了多个数据库连接,则调用getConnection()方法传入时参数不同,则返回不同的数据库连接
@Test
public void testDriver() throws SQLException {
//1、创建一个Driver实现类对象
Driver driver = new com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver();
//2、准备连接数据库的基本信息:url,user,password
String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.1:3306/test?serverTimezone=GMT";
Properties info = new Properties();
info.put("user", "root");
info.put("password", "password");
//3、调用Driver接口的connect(url,info)获取数据库连接
Connection connection = driver.connect(url, info);
System.out.println(connection);
}
3、通过DriverManager实现与数据库的连接,DriverManager是驱动的管理类
@Test
public void testDriverManager() throws SQLException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
String driverClass = null;
String jdbcUrl = null;
String user = null;
String password = null;
//1、读取类路径下的jdbc.properties 文件
InputStream in = getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
driverClass = properties.getProperty("driver");
jdbcUrl = properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
user = properties.getProperty("user");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
//2、加载数据库驱动程序
Class.forName(driverClass);
//3、通过DriverManager的getConnection()方法 获取数据库连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, user, password);
System.out.println(connection);
}
4、对获取连接的封装
@Test
public void testGetConnection2() throws Exception {
System.out.println(getConnection2());
}
public Connection getConnection2() throws Exception {
//1、准备连接数据库的4个字符串
//1)创建Properties对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
//2)获取jdbc.properties对应的输入流
InputStream in =
this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
//3)加载2)对应的输入流
properties.load(in);
//4)具体决定user,password等4个字符串
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String jdbcUrl = properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
//2、加载数据库驱动程序(对应的Driver实现类中有注册驱动的静态代码块)
Class.forName(driver);
//3、通过DriverManager的getConnection()方法获取数据库连接
return DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, user, password);
}
二、执行SQL插入语句
1、通过JDBC向指定的数据表中插入一条记录
1.1 Statement: 用于执行SQL语句的对象
- 1)通过Connection的createStatement()方法来获取
- 2)通过executeUpdate(sql)可以执行SQL语句
- 3)传入的SQL可以是 insert delete update,但不能是select
1.2 Connection和Statement都是应用程序和数据库服务器的连接资源,使用后一定要关闭
- 要是有异常,可以在finally中关闭
1.3 关闭的顺序,先关闭后获取的,即先关闭Statement,后关闭Connection
@Test
/**
* 通过JDBC向指定的数据表中插入一条记录
* 1、Statement:用于执行SQL语句的对象
* 1)通过Connection的createStatement()方法来获取
* 2)通过executeUpdate(sql)可以执行SQL语句
* 3)传入的SQL可以是 insert delete update,但不能是select
*
* 2、Connection和Statement都是应用程序和数据库服务器的连接资源,使用后一定要关闭
* 1)要是有异常,可以在finally中关闭
*
* 3、关闭的顺序,先关闭后获取的,即先关闭Statement,后关闭Connection
*
*/
public void testStatement() throws Exception {
//1、获取数据库连接
Connection conn = getConnection2();
//3、准备插入SQL语句
String sql = "INSERT INTO customer(NAME,EMAIL,BIRTH) "
+ "VALUES('xyz','xyz@atguigu.com','1991-10-25')";
//4、执行插入
//1)获取操作 SQL 语句的 Statement对象,
//调用Connection的createStatement()方法来获取
Statement statement = conn.createStatement();
//2)调用Statement对象的executeUpdate(sql)执行SQL语句进行插入
statement.executeUpdate(sql);
//5、关闭Statement对象
statement.close();
//2、关闭连接
conn.close();
}
2、数据库更新,包括insert update delete
public void update(String sql) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement statement = null;
try {
conn = JDBCTools.getConnection();
statement = conn.createStatement();
statement.executeUpdate(sql);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JDBCTools.release(statement, conn);
}
}
3、查询的实现
-
ResultSet:结果集,封装了使用JDBC查询的结果
-
1、调用Statement对象的executeQuery(sql)可以得到结果集
-
2、ResultSet返回的实际上就是一张数据表,有一个指针指向数据表的第一行的前面,可以调用next()方法检测 下一行是否有效,有效返回True,且指针下移,相当于Iterator对象的hasNext()和next()方法的结合体
-
3、当指针对位到一行时,可以通过getXxx(index)或者getXxx(columnName)获取每一列的值, 如getInt(1),getString(“name”)
-
4、ResultSet也需要关闭
/**
* ResultSet:结果集,封装了使用JDBC查询的结果
* 1、调用Statement对象的executeQuery(sql)可以得到结果集
* 2、ResultSet返回的实际上就是一张数据表,有一个指针指向数据表的第一行的前面,可以调用next()方法检测下一行是否有效,
* - 有效返回True,且指针下移,相当于Iterator对象的hasNext()和next()方法的结合体
* 3、当指针对位到一行时,可以通过getXxx(index)或者getXxx(columnName)获取每一列的值,
* - 如getInt(1),getString("name")
* 4、ResultSet也需要关闭
*/
@Test
public void testResultSet() {
//获取id=1的customers数据表的记录。并打印
Connection conn = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//1. 获取Connection
conn = JDBCTools.getConnection();
//2. 获取Statement
statement = conn.createStatement();
//3. 准备SQL
String sql = "SELECT id,NAME,EMAIL,BIRTH "
+ "FROM customer ";
//4. 执行查询,得到ResultSet
rs = statement.executeQuery(sql);
//5. 处理ResultSet
while(rs.next()) {
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString("name");
String email = rs.getString(3);
Date birth = rs.getDate(4);
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(email);
System.out.println(birth);
}
//6、关闭数据库资源
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JDBCTools.release(rs, statement, conn);
}
}
补充JDBCTools.java:
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* @author User
* 1、操作JDBC的工具类,其中封装了一些工具方法
*
*/
public class JDBCTools {
public static void release(ResultSet rs,
Statement statement, Connection conn) {
if(rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 1.关闭Statement和Connection
* @param statement
* @param conn
*/
public static void release(Statement statement, Connection conn) {
if(statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
*
* 1、获取数据连接的方法
* 通过读取配置文件从数据库服务器获取一个连接
*
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
//1、准备连接数据库的4个字符串
//1)创建Properties对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
//2)获取jdbc.properties对应的输入流
InputStream in =
JDBCTools.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
//3)加载2)对应的输入流
properties.load(in);
//4)具体决定user,password等4个字符串
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String jdbcUrl = properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
String driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
//2、加载数据库驱动程序(对应的Driver实现类中有注册驱动的静态代码块)
Class.forName(driver);
//3、通过DriverManager的getConnection()方法获取数据库连接
return DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl, user, password);
}
}
三、Preparedstatement代替Statement
1.Preparedstatement:是statement的子接口,可以传入带占位符的SQL 语句. 并且提供了补充占位符变量的方法.可防SQL注入,提高性能(可传入占位符,可预编译)
2.使用PreparedStatement.
1).创建PreparedStatement:
string sql="INSERT INTO examstudent VALUES(?,?,?,?,?,?,?)
PreparedStatement ps=conn.preparestatement(sql);
调动 Preparedstatement的setxxx(int index,object val)设置占位符的值index 值从1开始.
2).执行SQL语句:executeQuery()或executeUpdate().注意:执行时不再需要传入SQL 语句.
@Test
public void testPreparedStatement() {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
conn = JDBCTools.getConnection();
String sql = "INSERT INTO customer(NAME,EMAIL,BIRTH) "
+ "VALUES(?,?,?)";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, "Kally");
ps.setString(2, "kly@163.com");
ps.setDate(3, new Date(new java.util.Date().getTime())) ;
ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JDBCTools.release(ps, conn);
}
}
四、SQL注入示例
1、SQL注入
/**
* SQL 注入.
*/
@Test
public void testSQLInjection() {
String username = "a' OR PASSWORD = ";
String password = " OR '1'='1";
String sql = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = '" + username
+ "' AND " + "password = '" + password + "'";
System.out.println(sql);
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JDBCTools.getConnection();
statement = connection.createStatement();
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
if (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println("登录成功!");
} else {
System.out.println("用户名和密码不匹配或用户名不存在. ");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCTools.release(resultSet, statement, connection);
}
}
2、使用prepareStatement防SQL注入
@Test
public void testInjection2() {
String username = "a' OR PASSWORD = ";
String password = " OR '1'='1";
String sql = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = ?"
+ " AND password = ?";
System.out.println(sql);
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JDBCTools.getConnection();
ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, username);
ps.setString(2, password);
resultSet = ps.executeQuery();
if (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println("登录成功!");
} else {
System.out.println("用户名和密码不匹配或用户名不存在. ");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCTools.release(resultSet, ps, connection);
}
}
五、元数据
1、ResultSetMetaData:描述结果集的元数据
Java通过JDBC获得连接以后,得到一个Connection对象,可以从这个对象获得有关数据库管理系统的各种信息,包括数据库中的各个表,表中的各个列,数据类型,触发器,存储过程等各方面的信息.
根据这些信息,JDBC可以访问一个实现事先并不了解的数据库. 获取这些信息的方法都是在DatabaseMetaData类的对象上实现的,而 DataBaseMetaData对象是在Connection对象上获得的.
/**
* ResultSetMetaData描述结果集的元数据
* 可以得到结果集中的基本信息:结果集中哪些列,列名,列的别名
*/
@Test
public void testResultSetMetaData() {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = JDBCTools.getConnection();
String sql = "SELECT id,name costomerName,email,birth "
+ "FROM customer";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
//1、得到ResultSetMetaData对象
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
//2、得到列的个数
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
System.out.println(columnCount);
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++) {
//3、得到列名
String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i + 1);
//4、得到列的别名
String columnLabel = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1);
System.out.println(columnName + "," + columnLabel);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JDBCTools.release(rs, ps, conn);
}
}
2、取得数据库自动生成的主键
/**
* 取得数据库自动生成的主键
*/
@Test
public void testGetKeyValue() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JDBCTools.getConnection();
String sql = "INSERT INTO customer(name, email, birth)" +
"VALUES(?,?,?)";
// preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//使用重载的 prepareStatement(sql, flag)
//来生成 PreparedStatement 对象
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql,
Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "ABCDE");
preparedStatement.setString(2, "abcde@163.com");
preparedStatement.setDate(3,
new Date(new java.util.Date().getTime()));
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
//通过 getGeneratedKeys() 获取包含了新生成的主键的 ResultSet 对象
//在 ResultSet 中只有一列 GENERATED_KEY, 用于存放新生成的主键值.
ResultSet rs = preparedStatement.getGeneratedKeys();
if(rs.next()){
System.out.println(rs.getObject(1));
}
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
for(int i = 0; i < rsmd.getColumnCount(); i++){
System.out.println(rsmd.getColumnName(i + 1));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
JDBCTools.release(null, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
六、LOB
1、LOB
Large Objects(大对象),是用来存储大量的二进制和文本数据的一种数据类型(一个LOB字段可存储可多达4GB的数据).
LOB分为两种类型:内部LOB和外部LOB.
内部LOB将数据以字节流的形式存储在数据库的内部. 因而,内部LOB的许多操作都可以参与事务,也可以像处理普通数据一样对其进行备份和反复操作.
Oracle支持三种类型的内部LOB:
- BLOB(二进制数据)
- CLOB(单字节字符数据) NCLOB(多字节字符数据).
CLOB和NCLOB类型适用于存储超长的文本数据,BLOB字段适用于存储大量的二进制数据,如图像、视频、音频,文件等.
目前只支持一种外部LOB类型,即BFILE类型.在数据库内,该类型仅存储数据在操作系统中的位置信息, 而数据的实体以外部文件的形式存在于操作系统的文件系统中.因而,该类型所表示的数据是只读的,不参与事务. 该类型可帮助用户管理大量的由外部程序访问的文件.
MySQL中,BLOB是一个二进制大型对象,是一个可以存储大量数据的容器,它能容纳不同大小的数据. MySQL的四种BLOB类型(除了在存储的最大信息量上不同外,他们是等同的)
实际使用中根据需要存入的数据大小定义不同的BLOB类型. 需要注意的是:如果存储的文件过大,数据库的性能会下降.
类型大小(单位:字节)
- TinyBlob 最大255
- Blob最大65K
- MediumBlob 最大16M
- LongBlob 最大4G
2、写 blob 数据
在 Mysql 新建一列,类型设置为blob或longblob
/**
* 插入 BLOB 类型的数据必须使用 PreparedStatement:因为 BLOB 类型
* 的数据时无法使用字符串拼写的。
*
* 调用 setBlob(int index, InputStream inputStream)
*/
@Test
public void testInsertBlob(){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JDBCTools.getConnection();
String sql = "INSERT INTO customer(name, email, birth, picture)"
+ "VALUES(?,?,?,?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "ABC");
preparedStatement.setString(2, "abc@163.com");
preparedStatement.setDate(3,
new Date(new java.util.Date().getTime()));
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("Flower.jpg");
preparedStatement.setBlob(4, inputStream);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
JDBCTools.release(null, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
``
### 3、读取 blob 数据
```java
/**
* 读取 blob 数据:
* 1. 使用 getBlob 方法读取到 Blob 对象
* 2. 调用 Blob 的 getBinaryStream() 方法得到输入流。再使用 IO 操作即可.
*/
@Test
public void readBlob(){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JDBCTools.getConnection();
String sql = "SELECT id, name customerName, email, birth, picture "
+ "FROM customer WHERE id = 8";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
if(resultSet.next()){
int id = resultSet.getInt(1);
String name = resultSet.getString(2);
String email = resultSet.getString(3);
System.out.println(id + ", " + name + ", " + email);
Blob picture = resultSet.getBlob(5);
InputStream in = picture.getBinaryStream();
System.out.println(in.available());
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("flower2.jpg");
byte [] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len = in.read(buffer)) != -1){
out.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
in.close();
out.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
JDBCTools.release(resultSet, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
七、事务
1、事务原子性
/**
* Tom 给 Jerry 汇款 500 元.
*
* 关于事务:
* 1. 如果多个操作, 每个操作使用的是自己的单独的连接, 则无法保证事务.
* 2. 具体步骤: 1). 事务操作开始前, 开始事务:
* 取消 Connection 的默认提交行为. connection.setAutoCommit(false);
* 2). 如果事务的操作都成功,
* 则提交事务: connection.commit();
* 3). 回滚事务: 若出现异常, 则在 catch 块中回滚事务:
*/
@Test
public void testTransaction() {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCTools.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection.getAutoCommit());
// 开始事务: 取消默认提交.
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql = "UPDATE users SET balance = "
+ "balance - 500 WHERE id = 1";
update(connection, sql);
//出现异常
int i = 10 / 0;
System.out.println(i);
sql = "UPDATE users SET balance = " + "balance + 500 WHERE id = 2";
update(connection, sql);
// 提交事务
connection.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 回滚事务
try {
connection.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
} finally {
JDBCTools.release(null, null, connection);
}
public void update(Connection connection, String sql, Object... args) {
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCTools.release(null, preparedStatement, null);
}
}
2、隔离性级别
/**
* 测试事务的隔离级别 在 JDBC 程序中可以通过 Connection 的 setTransactionIsolation 来设置事务的隔离级别.
*/
@Test
public void testTransactionIsolationUpdate() {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCTools.getConnection();
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql = "UPDATE users SET balance = "
+ "balance - 500 WHERE id = 1";
update(connection, sql);
connection.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
}
}
@Test
public void testTransactionIsolationRead() {
String sql = "SELECT balance FROM users WHERE id = 1";
Integer balance = getForValue(sql);
System.out.println(balance);
}
// 返回某条记录的某一个字段的值 或 一个统计的值(一共有多少条记录等.)
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <E> E getForValue(String sql, Object... args) {
// 1. 得到结果集: 该结果集应该只有一行, 且只有一列
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 1. 得到结果集
connection = JDBCTools.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection.getTransactionIsolation());
// connection.setTransactionIsolation(Connection.TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED);
connection.setTransactionIsolation(Connection.TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED);
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
if (resultSet.next()) {
return (E) resultSet.getObject(1);
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCTools.release(resultSet, preparedStatement, connection);
}
// 2. 取得结果
return null;
}
3、Mysql中的隔离级别
在MySql中设置隔离级别
每启动一个mysql程序,就会获得一个单独的数据库连接每个数据库连接都有一个全局变量
@@tx_isolation
表示当前的事务隔离级别.
MySQL默认的隔离级别为Repeatable Read
查看当前的隔离级别:
SELECT @@tx isolation;
设置当前mySQL连接的隔离级别:
set transaction isolation level read commited;
设置数据库系统的全局的隔离级别:
set globaltransaction isolation level read commited;
八、批量处理的性能问题
向Oracle 的 customers 数据表中插入 10 万条记录,测试如何插入, 用时最短.
1、使用 Statement.
@Test
public void testBatchWithStatement(){
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
String sql = null;
try {
connection = JDBCTools.getConnection();
JDBCTools.beginTx(connection);
statement = connection.createStatement();
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0; i < 100000; i++){
sql = "INSERT INTO customers VALUES(" + (i + 1)
+ ", 'name_" + i + "', '29-6月 -13')";
statement.addBatch(sql);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Time: " + (end - begin)); //39567
JDBCTools.commit(connection);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
JDBCTools.rollback(connection);
} finally{
JDBCTools.releaseDB(null, statement, connection);
}
}
用时:39567
2、使用PreparedStatement,有预编译
@Test
public void testBatchWithPreparedStatement(){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
String sql = null;
try {
connection = JDBCTools.getConnection();
JDBCTools.beginTx(connection);
sql = "INSERT INTO customers VALUES(?,?,?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
Date date = new Date(new java.util.Date().getTime());
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0; i < 100000; i++){
preparedStatement.setInt(1, i + 1);
preparedStatement.setString(2, "name_" + i);
preparedStatement.setDate(3, date);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Time: " + (end - begin)); //9819
JDBCTools.commit(connection);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
JDBCTools.rollback(connection);
} finally{
JDBCTools.releaseDB(null, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
用时:9819
3、使用Batch,相当于集中分批处理
@Test
public void testBatch(){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
String sql = null;
try {
connection = JDBCTools.getConnection();
JDBCTools.beginTx(connection);
sql = "INSERT INTO customers VALUES(?,?,?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
Date date = new Date(new java.util.Date().getTime());
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0; i < 100000; i++){
preparedStatement.setInt(1, i + 1);
preparedStatement.setString(2, "name_" + i);
preparedStatement.setDate(3, date);
//"积攒" SQL
preparedStatement.addBatch();
//当 "积攒" 到一定程度, 就统一的执行一次. 并且清空先前 "积攒" 的 SQL
if((i + 1) % 300 == 0){
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
preparedStatement.clearBatch();
}
}
//若总条数不是批量数值的整数倍, 则还需要再额外的执行一次.
if(100000 % 300 != 0){
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
preparedStatement.clearBatch();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Time: " + (end - begin)); //569
JDBCTools.commit(connection);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
JDBCTools.rollback(connection);
} finally{
JDBCTools.releaseDB(null, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
九、数据库连接池
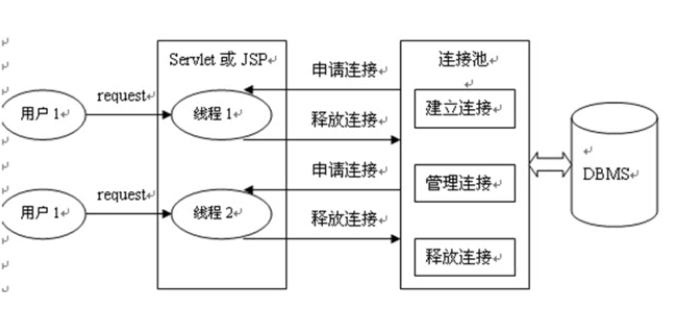
1、DBCB数据库连接池,手动设置
/**
* 使用 DBCP 数据库连接池
* 1. 加入 jar 包(2 个jar 包). 依赖于 Commons Pool
* 2. 创建数据库连接池
* 3. 为数据源实例指定必须的属性
* 4. 从数据源中获取数据库连接
* @throws SQLException
*/
@Test
public void testDBCP() throws SQLException{
final BasicDataSource dataSource = new BasicDataSource();
//2. 为数据源实例指定必须的属性
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("1230");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql:///atguigu");
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//3. 指定数据源的一些可选的属性.
//1). 指定数据库连接池中初始化连接数的个数
dataSource.setInitialSize(5);
//2). 指定最大的连接数: 同一时刻可以同时向数据库申请的连接数
dataSource.setMaxActive(5);
//3). 指定小连接数: 在数据库连接池中保存的最少的空闲连接的数量
dataSource.setMinIdle(2);
//4).等待数据库连接池分配连接的最长时间. 单位为毫秒. 超出该时间将抛出异常.
dataSource.setMaxWait(1000 * 5);
//4. 从数据源中获取数据库连接
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection.getClass());
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection.getClass());
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection.getClass());
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection.getClass());
Connection connection2 = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(">" + connection2.getClass());
//一个线程获取连接,一个线程sleep5500,最大等待时间是5000
new Thread(){
public void run() {
Connection conn;
try {
conn = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(conn.getClass());
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
};
}.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(5500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
connection2.close();
}
2、DBCB数据库连接池,加载配置文件
/**
* 1. 加载 dbcp 的 properties 配置文件: 配置文件中的键需要来自 BasicDataSource
* 的属性.
* 2. 调用 BasicDataSourceFactory 的 createDataSource 方法创建 DataSource
* 实例
* 3. 从 DataSource 实例中获取数据库连接.
*/
@Test
public void testDBCPWithDataSourceFactory() throws Exception{
Properties properties = new Properties();
InputStream inStream = JDBCTest.class.getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("dbcp.properties");
properties.load(inStream);
DataSource dataSource =
BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
System.out.println(dataSource.getConnection());
// BasicDataSource basicDataSource =
// (BasicDataSource) dataSource;
//
// System.out.println(basicDataSource.getMaxWait());
}
/**
username=root
password=1234
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql:///testDataBase
initialSize=10
maxActive=50
minIdle=5
maxWait=5000
*/
3、C3PO数据库连接池
@Test
public void testJdbcTools() throws Exception{
Connection connection = JDBCTools.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
}
/**
* 1. 创建 c3p0-config.xml 文件,
* 参考帮助文档中 Appendix B: Configuation Files 的内容
* 2. 创建 ComboPooledDataSource 实例;
* DataSource dataSource =
* new ComboPooledDataSource("helloc3p0");
* 3. 从 DataSource 实例中获取数据库连接.
*/
@Test
public void testC3poWithConfigFile() throws Exception{
DataSource dataSource =
new ComboPooledDataSource("helloc3p0");
System.out.println(dataSource.getConnection());
ComboPooledDataSource comboPooledDataSource =
(ComboPooledDataSource) dataSource;
System.out.println(comboPooledDataSource.getMaxStatements());
}
@Test
public void testC3P0() throws Exception{
ComboPooledDataSource cpds = new ComboPooledDataSource();
cpds.setDriverClass( "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" ); //loads the jdbc driver
cpds.setJdbcUrl( "jdbc:mysql:///testDataBase" );
cpds.setUser("root");
cpds.setPassword("1230");
System.out.println(cpds.getConnection());
}
/**
c3p0-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<c3p0-config>
<named-config name="helloc3p0">
<!-- 指定连接数据源的基本属性 -->
<property name="user">root</property>
<property name="password">1230</property>
<property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql:///atguigu</property>
<!-- 若数据库中连接数不足时, 一次向数据库服务器申请多少个连接 -->
<property name="acquireIncrement">5</property>
<!-- 初始化数据库连接池时连接的数量 -->
<property name="initialPoolSize">5</property>
<!-- 数据库连接池中的最小的数据库连接数 -->
<property name="minPoolSize">5</property>
<!-- 数据库连接池中的最大的数据库连接数 -->
<property name="maxPoolSize">10</property>
<!-- C3P0 数据库连接池可以维护的 Statement 的个数 -->
<property name="maxStatements">20</property>
<!-- 每个连接同时可以使用的 Statement 对象的个数 -->
<property name="maxStatementsPerConnection">5</property>
</named-config>
</c3p0-config>
*/
十、DBUtils
总述
-
- ResultSetHandler 的作用: QueryRunner 的 query 方法的返回值最终取决于query 方法的 ResultHandler 参数的 hanlde 方法的返回值.
-
- BeanListHandler: 把结果集转为一个 Bean 的 List, 并返回. Bean 的类型在 创建 BeanListHanlder 对象时以 Class 对象的方式传入. 可以适应列的别名来映射
- JavaBean 的属性名:
String sql = "SELECT id, name customerName, email, birth " +
"FROM customers WHERE id = ?";
-
BeanListHandler(Class
type) -
- BeanHandler: 把结果集转为一个 Bean, 并返回. Bean 的类型在创建 BeanHandler对象时以 Class 对象的方式传入BeanHandler(Class
type)
- BeanHandler: 把结果集转为一个 Bean, 并返回. Bean 的类型在创建 BeanHandler对象时以 Class 对象的方式传入BeanHandler(Class
-
- MapHandler: 把结果集转为一个 Map 对象, 并返回. 若结果集中有多条记录, 仅返回第一条记录对应的 Map 对象. Map 的键: 列名(而非列的别名), 值: 列的值
-
- MapListHandler: 把结果集转为一个 Map 对象的集合, 并返回.Map 的键: 列名(而非列的别名),值: 列的值
-
- ScalarHandler: 可以返回指定列的一个值或返回一个统计函数的值.
1、QueryRunner 类
1.1 update方法
/**
* 测试 QueryRunner 类的 update 方法
* 该方法可用于 INSERT, UPDATE 和 DELETE
*/
@Test
public void testQueryRunnerUpdate() {
//1. 创建 QueryRunner 的实现类
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
String sql = "DELETE FROM customers " +
"WHERE id IN (?,?)";
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCTools.getConnection();
//2. 使用其 update 方法
queryRunner.update(connection,
sql, 12, 13);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
JDBCTools.releaseDB(null, null, connection);
}
}
1.2 query 方法
/**
* 测试 QueryRunner 的 query 方法
*/
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
@Test
public void testResultSetHandler(){
String sql = "SELECT id, name, email, birth " +
"FROM customers";
//1. 创建 QueryRunner 对象
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = JDBCTools.getConnection();
/**
* 2. 调用 query 方法:
* ResultSetHandler 参数的作用: query 方法的返回值直接取决于
* ResultSetHandler 的 hanlde(ResultSet rs) 是如何实现的. 实际上, 在
* QueryRunner 类的 query 方法中也是调用了 ResultSetHandler 的 handle()
* 方法作为返回值的。
*/
Object object = queryRunner.query(conn, sql,
new ResultSetHandler(){
@Override
public Object handle(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
List<Customer> customers = new ArrayList<>();
while(rs.next()){
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String name = rs.getString(2);
String email = rs.getString(3);
Date birth = rs.getDate(4);
Customer customer =
new Customer(id, name, email, birth);
customers.add(customer);
}
return customers;
}
}
);
System.out.println(object);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
JDBCTools.releaseDB(null, null, conn);
}
}
1.3 ResultSetHandler 的 BeanListHandler 实现类
/**
* 测试 ResultSetHandler 的 BeanListHandler 实现类
* BeanListHandler: 把结果集转为一个 Bean 的 List. 该 Bean
* 的类型在创建 BeanListHandler 对象时传入:
*
* new BeanListHandler<>(Customer.class)
*
*/
@Test
public void testBeanListHandler(){
String sql = "SELECT id, name customerName, email, birth " +
"FROM customers";
//1. 创建 QueryRunner 对象
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = JDBCTools.getConnection();
Object object = queryRunner.query(conn, sql,
new BeanListHandler<>(Customer.class));
System.out.println(object);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
JDBCTools.releaseDB(null, null, conn);
}
}
1.4 MapHandler
@Test
public void testMapHandler(){
Connection connection = null;
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
String sql = "SELECT id, name customerName, email, birth " +
"FROM customers WHERE id = ?";
try {
connection = JDBCTools.getConnection();
Map<String, Object> map = queryRunner.query(connection,
sql, new MapHandler(), 4);
System.out.println(map);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
JDBCTools.releaseDB(null, null, connection);
}
}
1.4.1 MapListHandler
@Test
public void testMapListHandler(){
Connection connection = null;
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
String sql = "SELECT id, name, email, birth " +
"FROM customers";
try {
connection = JDBCTools.getConnection();
List<Map<String, Object>> mapList = queryRunner.query(connection,
sql, new MapListHandler());
System.out.println(mapList);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
JDBCTools.releaseDB(null, null, connection);
}
}
1.5 ScalarHandler
```java
@Test public void testScalarHandler(){ Connection connection = null; QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
String sql = "SELECT name FROM customers " +
"WHERE id = ?";
try {
connection = JDBCTools.getConnection();
Object count = queryRunner.query(connection, sql,
new ScalarHandler(), 5);
System.out.println(count);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
JDBCTools.releaseDB(null, null, connection);
}
}
```